Principle of function
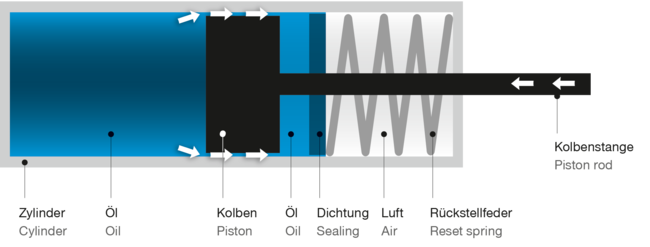
- In a closed housing a piston is moving back- and forward. A food-safe silicon-oil can flow in both directions through small channels. The viscosity of the oil, as well as the modification of the cross-section of the channels, leads to the friction needed to reduce the speed. The friction-heat will be channeled outside through the cylinder-wall.
- Highest energy-consumption on smallest cross section
- Different damping-characteristics possible
Fluid damper – Volume-compensation

- A: Volume-compensation by means of a spring in an air-filled chamber (ZIMMER-principle)
- B: Volume-adjustment by using a sponge (competitors)
Damper with and whitout reset-function
Damper without reset-function needs a coupler onto the pistonrod is needed to be used within the fitting. The pistonrod do not extract by itself, it has to be extracted manually.
Damper with a integrated reset-function a Coupler is not needed onto the pistonrod within the fitting. The pistonrod will be extracted automatically.

without reset- function

with integrated reset- function
FLUID DAMPER TYPES
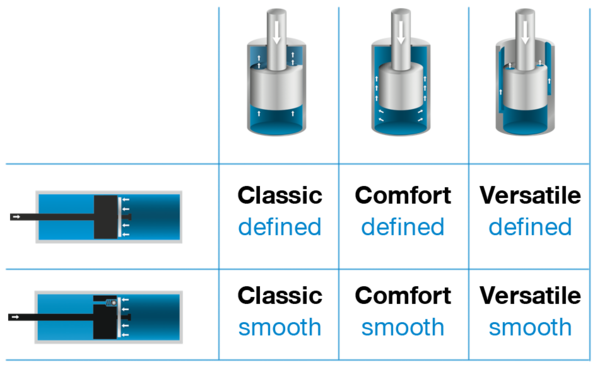
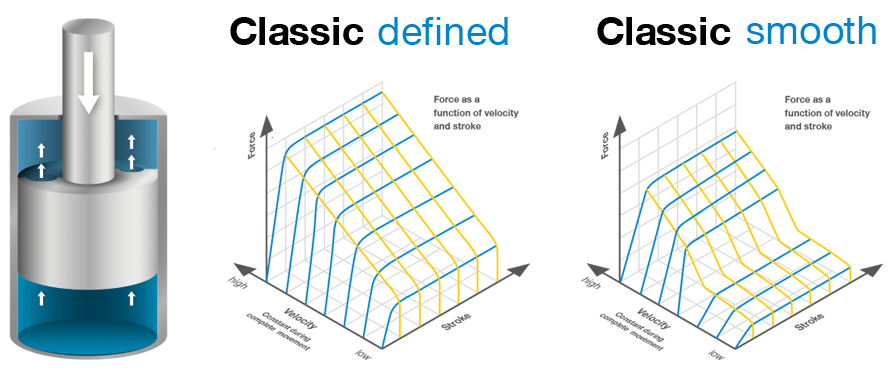
defined: speed independent
smooth: depending on speedless opening time constant closing picture small opening force
Fluid damper Classic
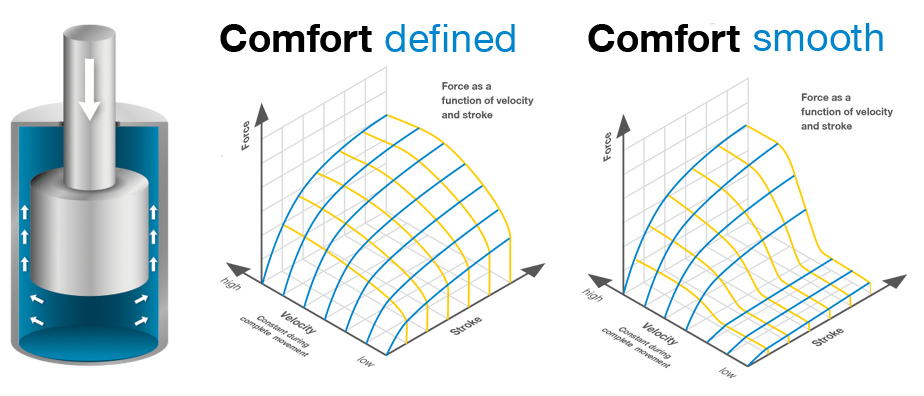
Fluid damper Comfort
Fluid damper Versatile
Through these two nozzles the oil can flow constantly. Channels in the housing enhances special cross-sections. Within this example the cross-section becomes smaller during retraction; thus the damping force becomes stronger
- Various damper-characteristics possible
- Force can be modified by varying the cross-section and by changing the number of the channels
smooth: Smooth reaction at low velocities
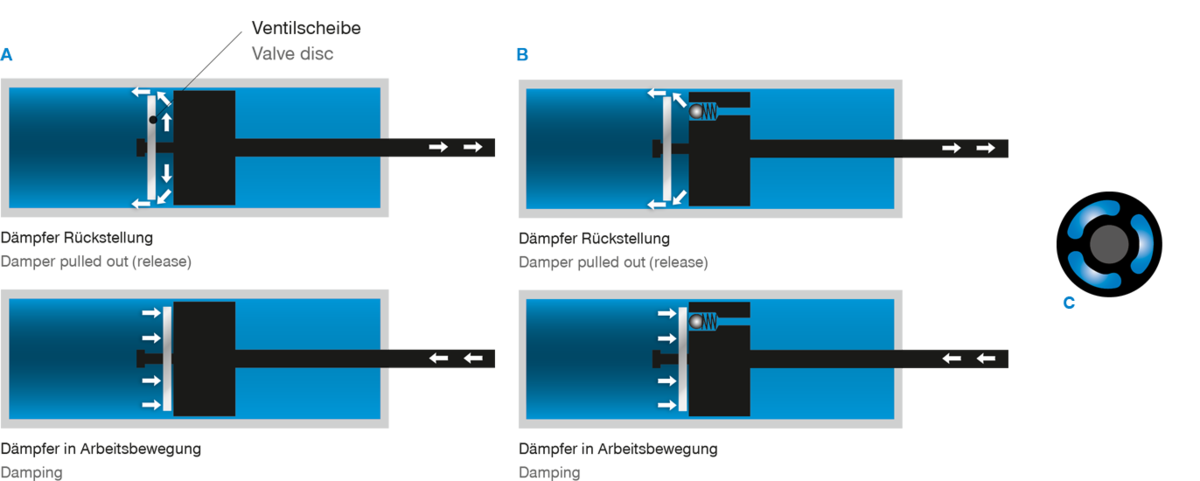
Fluid dampfer – Opening-movement
Valve disc as well as drillings lead to a minimalized resistance at opening and the damping force needed during closing-movement.
A: Piston defined
B: Piston smooth
C: Bunch-shaped drillings
(max. flow cross-section by means of elongated holes)
Comparsation defined/smooth in self- closing unit
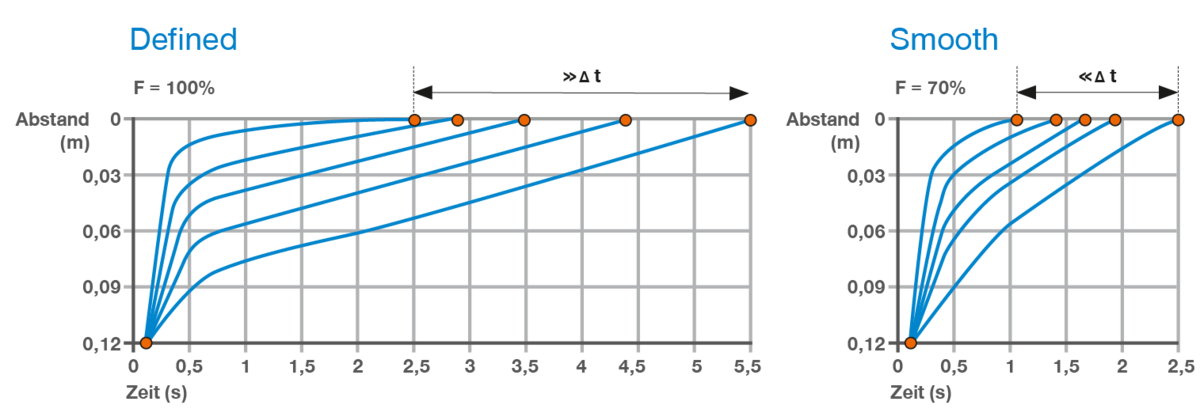
ExampleCharacteristicChiuso 100
load:
70kg sliding door
chart shows the closing time from 0,1–0,5 m/s in different graphs
Opening force is reduced about 30% in version:
smooth
Fluid damper characteristic with constant speed

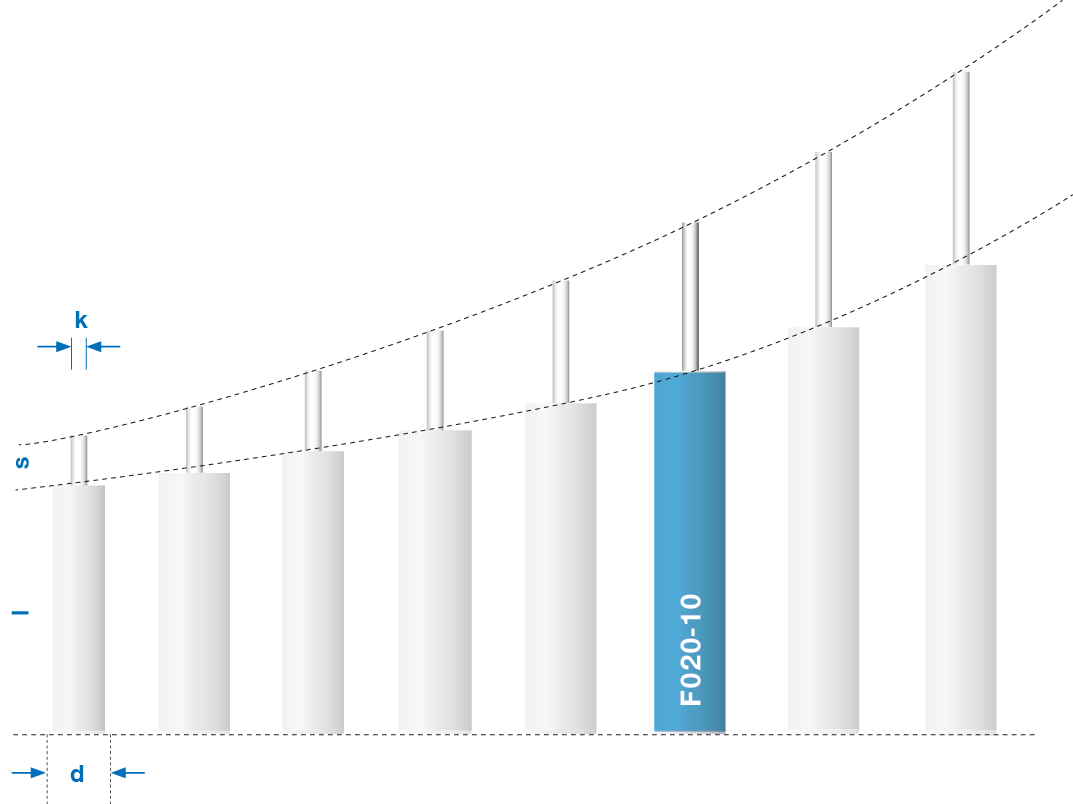
Product range damper Classic
- Housing length (l) 42 mm bis 67 mm
- Housing diameter (d) 6 mm, 8 mm und 10 mm
- Stroke (s) 5 mm bis 30 mm
- Piston rod diameter (k) 2,3 mm
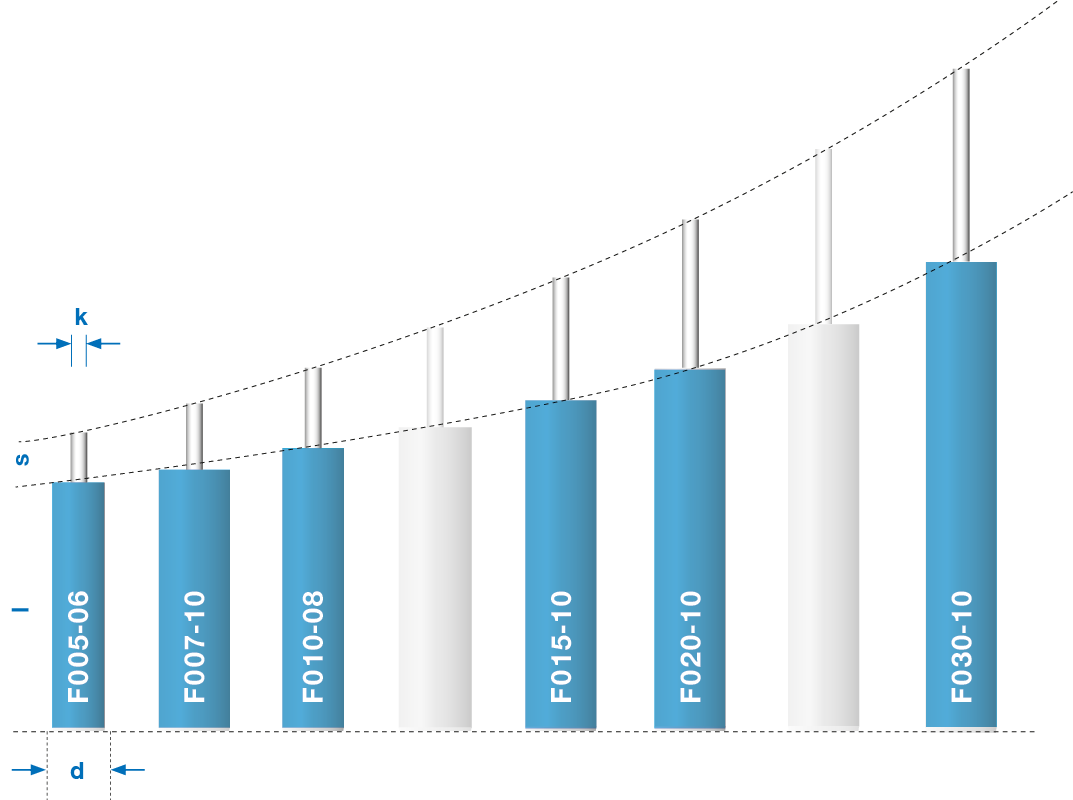
Product range damper Comfort
- Housing length (l) 29,5 mm bis 151,6 mm
- Housing diameter (d) 6 mm, 8 mm und 10 mm
- Stroke (s) 10 mm bis 100 mm
- Piston rod diameter (k) 1,5 bis 2,3 mm
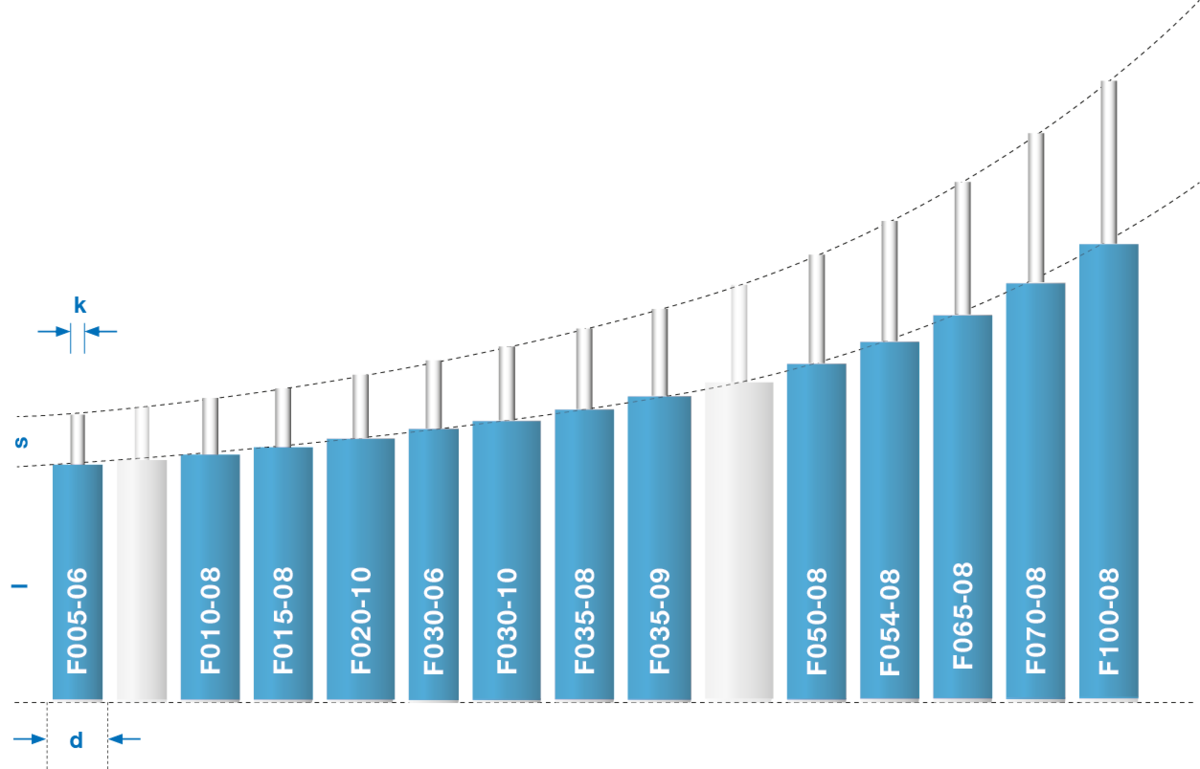
Product range damper Versatile
- Housing length (l) 42 mm bis 67 mm
- Housing diameter (d) 6 mm, 8 mm und 10 mm
- Stroke (s) 5 mm bis 30 mm
- Piston rod diameter (k) 2,3 mm